The 4Cs Guide
When purchasing a diamond, understanding the 4Cs—Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat Weight—is essential. These characteristics determine a diamond's quality, beauty, and value.
The 4Cs Guide
When purchasing a diamond, understanding the 4Cs—Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat Weight—is essential. These characteristics determine a diamond's quality, beauty, and value.
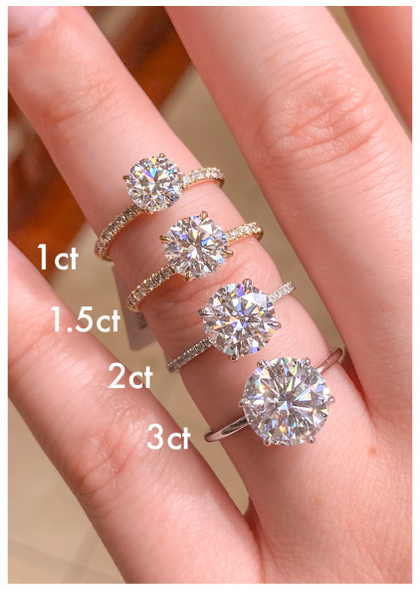


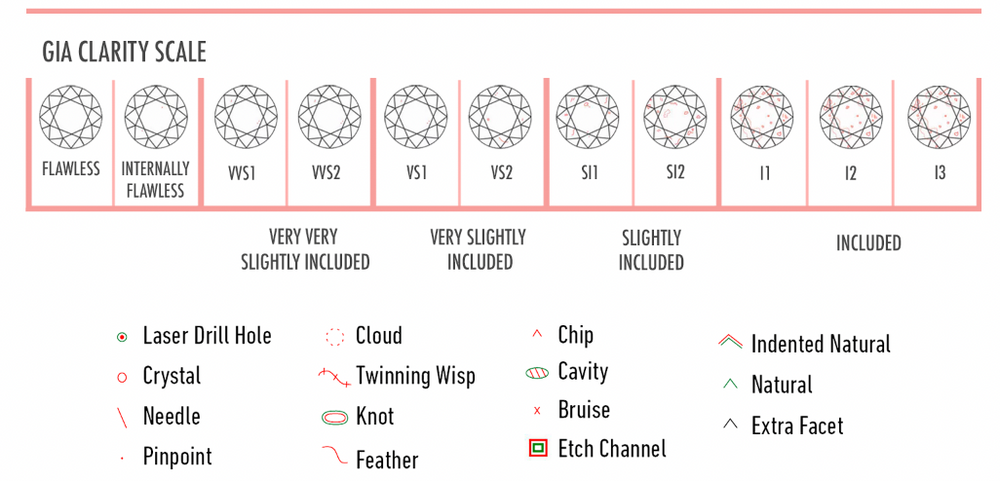
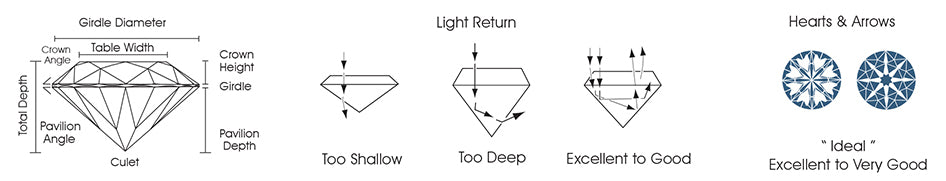
At our store, we specialize in colorless diamonds, ranging from D to F in color grade, with clarity levels from Flawless to VS2. Additionally, we prioritize diamonds with excellent or ideal cuts.
Understanding the 4Cs—Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat Weight—is crucial as they determine a diamond's quality, beauty, and value. Each C contributes to the overall appearance and value of the diamond, so it's essential to consider them when making a purchase.
The best diamond shape ultimately depends on personal preference. Popular shapes include round, princess, cushion, emerald, and oval. It's essential to choose a shape that reflects your style and fits well with the design of the ring.
Natural diamonds are formed deep within the earth over millions of years, while lab-grown diamonds are created in controlled environments using advanced technology. Both types of diamonds have similar physical and chemical properties but differ in their origin and price.
Fluorescence is a natural phenomenon where a diamond emits a soft glow when exposed to ultraviolet light. It primarily pertains to natural diamonds and is graded on a scale from None to Very Strong. While fluorescence can affect a natural diamond's appearance in certain lighting conditions, it does not always necessarily impact its beauty or value.
A diamond certificate, also known as a grading report, provides an independent assessment of a diamond's characteristics, including the 4Cs, fluorescence, and measurements. It helps verify the quality and authenticity of the diamond and is essential for insurance purposes.
Determine your priorities among the 4Cs based on your preferences and budget. For example, you may prioritize cut for maximum sparkle or color for a specific hue. By contacting us we can help you find the best diamond within your budget.
The color of your setting can significantly impact how your diamond appears. Generally, white gold and platinum settings complement colorless diamonds, enhancing their color and brilliance. On the other hand, yellow gold and rose gold settings can impart a warm tint to the diamond, which some individuals appreciate for its unique character.
For those who desire the icy-clear appearance of a colorless diamond but still love the warmth of yellow or rose gold, a two-tone setting can be an ideal solution. In a two-tone setting, the head of the setting is typically crafted from white gold or platinum, while the body is made in the metal color of your choice. This combination allows you to enjoy the warmth of yellow or rose gold while maintaining the desired colorlessness of your diamond.
Ultimately, the choice of setting color is a matter of personal preference. Some individuals adore the subtle warmth that yellow or rose gold imparts to their diamond, while others prefer the pristine clarity of a colorless diamond against a white gold or platinum setting.
The value retention of lab-grown diamonds over time is a subject of ongoing debate within the diamond industry. In our opinion, diamonds, whether lab-grown or natural, are not typically considered ideal investments for financial purposes. Instead, they are more akin to wearable art, symbolizing love and commitment.
When considering the potential resale value of a diamond, it's essential to understand that you are unlikely to recoup the full purchase price, especially if you are selling the diamond as raw materials rather than to someone for use as an engagement ring or other jewelry piece.
In general, if you were to sell a lab-grown or natural diamond later, you would likely not receive more money than what you initially paid. However, it's common to lose a significant portion of the diamond's value, typically ranging from 60% to 80% if selling it for its raw materials.
Comparing lab-grown and natural diamonds, the potential loss in value may be lower with a lab-grown diamond. For example, you could purchase a 2-carat D-VS1 XXX Round Lab Diamond for $2,750 brand new, whereas a 2-carat D VS1 XXX Round Natural Diamond might cost $25,130.
In this scenario, the estimated return you might receive for the natural diamond could be around $15,000, whereas for the lab-grown diamond, it might be $1,600. Even if you were to receive nothing for the lab-grown diamond, the overall loss would likely be significantly less compared to the natural diamond. You could expect to lose about $10,000 overall with the natural diamond, whereas the loss with the lab-grown diamond might range from $2,700 to $1,100.