Lab-Grown Diamonds Guide
Welcome to our Lab-Grown Diamonds page, where we demystify the brilliance of lab-created gems and help you make an informed decision for your jewelry needs.
Lab-Grown Diamonds Guide
Welcome to our Lab-Grown Diamonds page, where we demystify the brilliance of lab-created gems and help you make an informed decision for your jewelry needs.

Why Choose Lab-Grown Diamonds?
The Creation Process:
Lab-grown diamonds are created using advanced technological processes that mimic the natural conditions under which diamonds form deep within the Earth's mantle. High-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD) are the two primary methods used to grow diamonds in the lab.
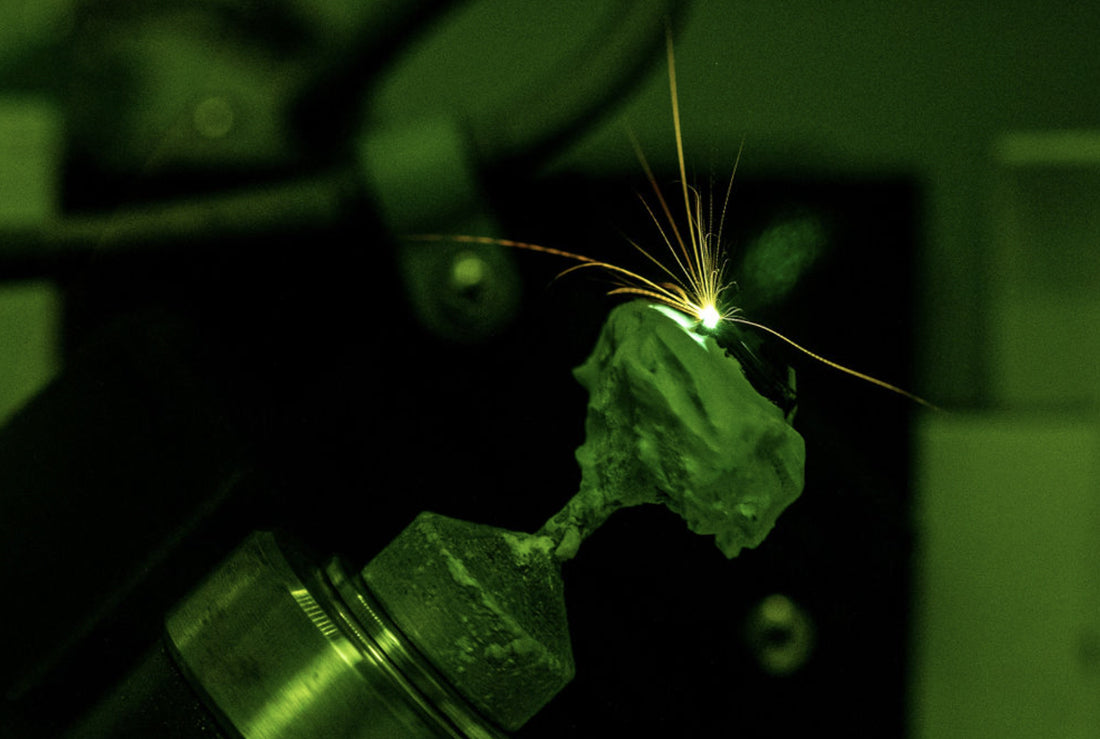
HPHT, or High-Pressure High-Temperature, is one of the methods used to create lab-grown diamonds. This process simulates the natural conditions under which diamonds form deep within the Earth's mantle. In the HPHT method, a small diamond seed is placed in a press and subjected to high temperatures (over 1,400°C) and high pressures (around 5-6 GPa), akin to those found hundreds of kilometers below the Earth's surface.
Under these extreme conditions, carbon atoms in a diamond seed crystal arrange themselves into a crystal lattice structure, gradually growing into a larger diamond over time. The process can take several days or weeks, depending on the desired size of the diamond. Once grown, the diamond is carefully cut, polished, and graded to ensure it meets the highest quality standards.
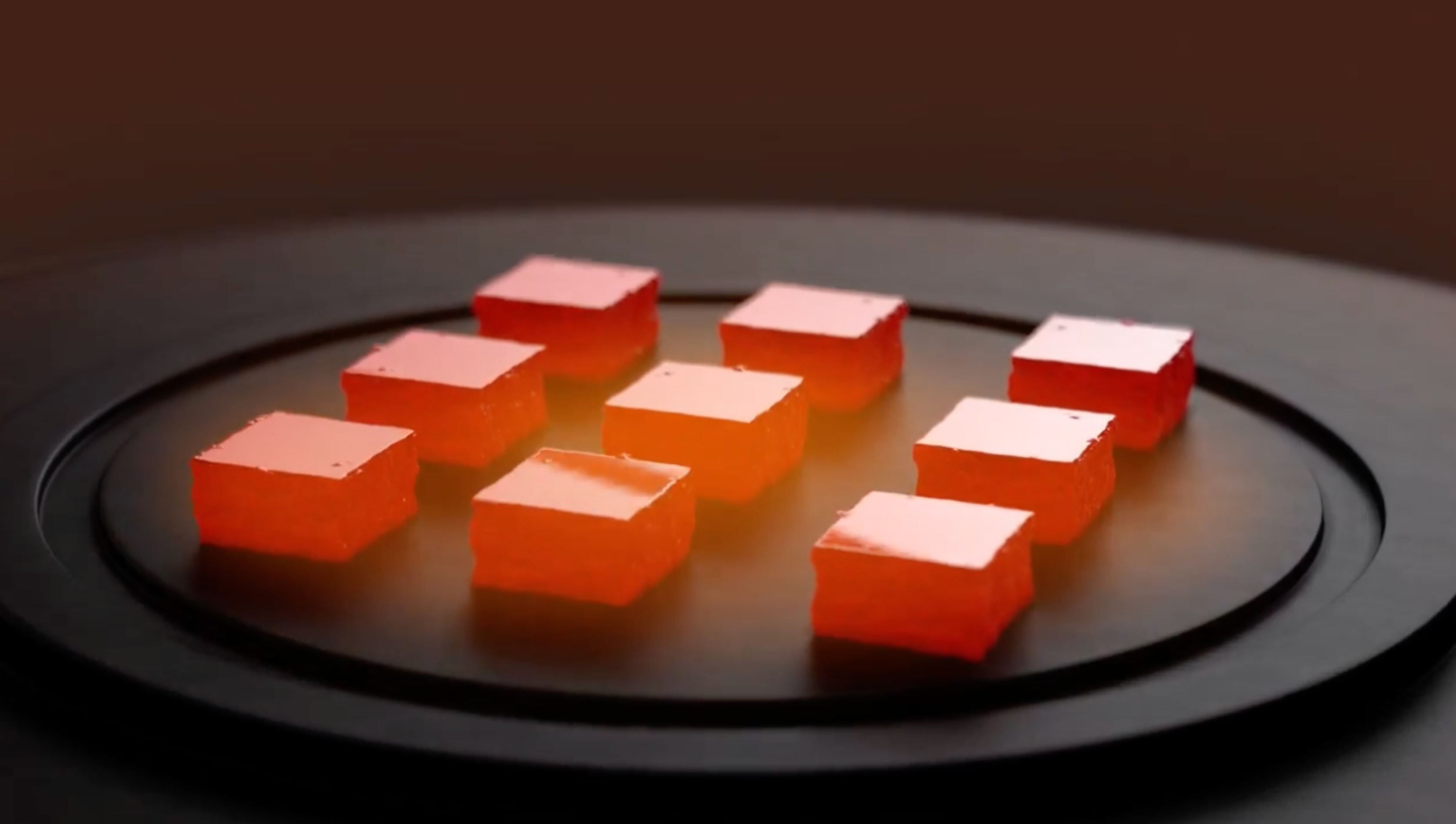

CVD, or Chemical Vapor Deposition, is another method used to create lab-grown diamonds. Unlike the HPHT method, which mimics the natural diamond-forming process, CVD involves a chemical process that occurs in a vacuum chamber.
In the CVD process, a diamond seed, typically a thin slice of diamond, is placed in a vacuum chamber along with a gas mixture containing carbon-rich gases like methane. When the chamber is heated, the gases break down, releasing carbon atoms. These carbon atoms then adhere to the diamond seed, gradually building up layer by layer to form a larger diamond crystal.
The CVD process allows for greater control over the growth of the diamond, resulting in diamonds with exceptional purity and uniformity. It also enables the creation of complex shapes and sizes, making it ideal for producing diamonds for various industrial and technological applications.
Lab-Grown vs. Natural Diamonds
Similarities:
Differences:
In summary, while lab-grown and natural diamonds share many similarities in terms of chemical composition, optical properties, and durability, their origin, cost, and ethical considerations distinguish them from one another. Whether you choose a lab-grown or natural diamond ultimately depends on your personal preferences, values, and budget.
In summary, while lab-grown and natural diamonds share many similarities in terms of chemical composition, optical properties, and durability, their origin, cost, and ethical considerations distinguish them from one another. Whether you choose a lab-grown or natural diamond ultimately depends on your personal preferences, values, and budget.